FMHS Everything Teaching
FMHS Everything Teaching
Achieving alignment
Constructive Alignment
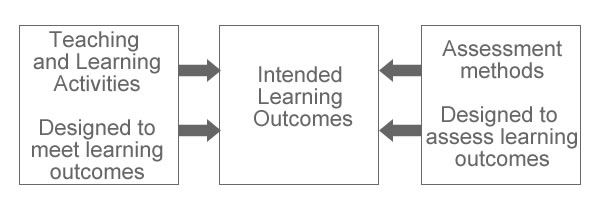
We can plan our teaching using the concept of constructive alignment. Constructive alignment states that the three main elements of the teaching process (learning outcomes, teaching and learning activities, and student assessment) must be aligned. Alignment occurs when there are clear and logical connections between these three components:
- learning outcomes (what you want students to know, understand, be able to do)
- learning activities (tasks, interactions etc. to enable students to achieve outcomes)
- student assessment (to measure whether students have achieved the intended outcomes).
The steps involved in the alignment of course learning outcomes, methods and assessments can be summarised as follows:
- Define the intended learning outcomes;
- Choose teaching and learning activities that are likely to lead to the achievement of the intended learning outcomes; and
- Develop assessments that require students to demonstrate their achievement to the specified standard of learning expressed in the assessment criteria.
|
|
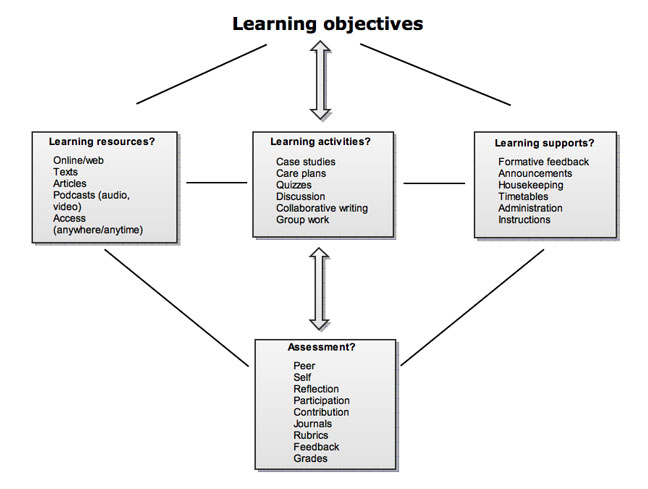
The diagram to the left is another way of understanding alignment and includes learning resources and learning supports - click on the image to see a larger version.
|
Adapted from Oliver, R. & Herrington, J. (2003). Exploring technology-mediated learning from a pedagogical perspective. Journal of Interactive Learning Environments, 11(2), 111-126.
Example: Tasking a History
- Learning outcome: Students will be able to obtain clear, comprehensive and relevant case histories.
- Teaching activities: Lecture on obtaining clear, comprehensive and relevant case histories; tutorial on obtaining clear, comprehensive and relevant case histories; clinical skills sessions in which students are paired to practice obtaining clear, comprehensive and relevant case histories; and supervised session with patient to practice obtaining clear, comprehensive and relevant case histories.
- Assessment: Students are assessed on their ability to obtain clear, comprehensive and relevant case histories.
In this example the activities enable students to achieve the intended learning outcome. Achievement consists of mastering a particular skill to a particular standard. The assessment must require students to demonstrate the skill at the desired standard.
 Check
Check
- Do I understand the concept of constructive alignment and how it relates to course design?
- Do I apply the concept of alignment when planning my courses?
Portfolio Possibilities